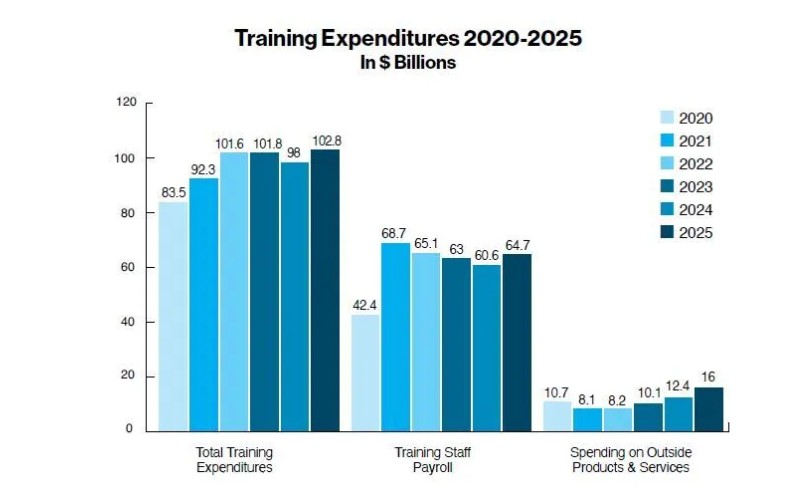
The latest industry report by Training magazine reveals renewed momentum in the U.S. training sector, with total companies spend on training employees increasing by nearly 5 percent as organizations continue to invest in skills, technology, and workforce development. Fueled by an influx of new companies, U.S. training expenditures reached $102.8 billion in 2025, up from $98 billion in 2024. Payroll climbed almost 7 percent to $64.7 billion, while spending on outside products and services surged 29 percent to $16 billion.
Average training budgets shifted slightly by company size: large companies decreased their spending from $13.3 million to $11.7 million; midsize companies remained steady at $1.6 million; and small companies declined from $374,207 to $333,305.
Although other training expenses (travel, facilities, equipment) fell to $22.1 billion, organizations continued to expand their use of learning tools and technologies, with average spending rising to $290,987, up from $268,397 last year.
Key takeaways
- Total training spend rebounded – Overall U.S. training expenditures increased 4.9% to $102.8 billion in 2025.
- Per-learner investment increased – Companies spent an average of $874 per learner, up from $774 in 2024.
- Spending varies by company size – Large firms: $468 per learner; midsize: $782; small firms: $1,091.
- Average training hours declined – Employees received 40 hours of training on average, down from 47 in 2024.
- External services and tech investment rose – Spending on outside products and services climbed 29% to $16 billion; learning tools averaged $290,987 per organization.
- AI and simulations gained traction – 49% plan to invest in games and simulations, 45% in online systems, and 37% now use AI in training.
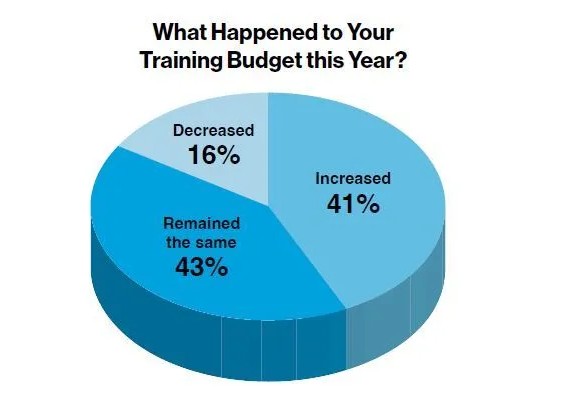
- Budgets stabilized with mixed adjustments – 41% of organizations increased budgets, 16% decreased them, and 43% held steady.
How much does it cost to train an employee in the U.S?
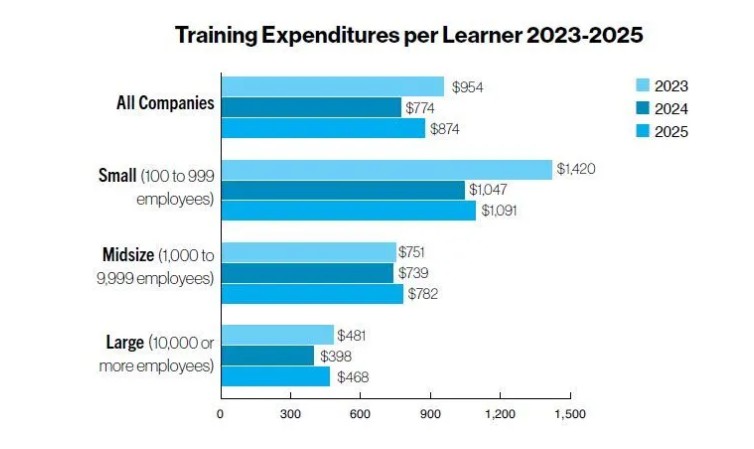
The average cost to train an employee rose notably this year, with companies spending $874 per learner in 2025, up from $774 in 2024. The increase reflects continued adoption of digital learning technologies and a stronger emphasis on workforce skills development.
When broken down by company size, large organizations spent $468 per learner, midsize firms spent $782, and small companies spent $1,091. Among industries, retailers and wholesalers reported the highest per-learner investment ($1,046), followed by services organizations ($944).
Despite higher costs, most companies cited efficiency improvements and broader reach through blended and online learning formats, suggesting that growth in spending is being offset by better scalability and learning outcomes.
Tools and technologies for learning
Investment in learning tools and technologies increased across most sectors, averaging 13 percent of training budgets, or $290,987 per organization (up from $268,397 in 2024). Large services and retail/wholesale organizations reported the biggest technology budgets—$2 million and $1.1 million, respectively.
Among anticipated purchases, games and simulations remain the top category, climbing to 49 percent from 46 percent last year. Online learning tools and systems increased to 45 percent (from 39 percent), business skills training rose to 44 percent (from 39 percent), and classroom tools and systems increased to 34 percent (from 29 percent).
Other categories saw moderate movement: courseware design remained steady at 33 percent; assessment and analysis testing decreased slightly to 30 percent; coaching and mentoring remained at 28 percent; and consulting increased to 26 percent. Augmented and virtual reality technologies gained ground, increasing to 10 percent from 8 percent in 2024.
Artificial intelligence continued its rapid ascent, with 37 percent of organizations using AI for training, up from 25 percent in 2024, reflecting growing confidence in adaptive learning and content automation.
Hours of training per employee
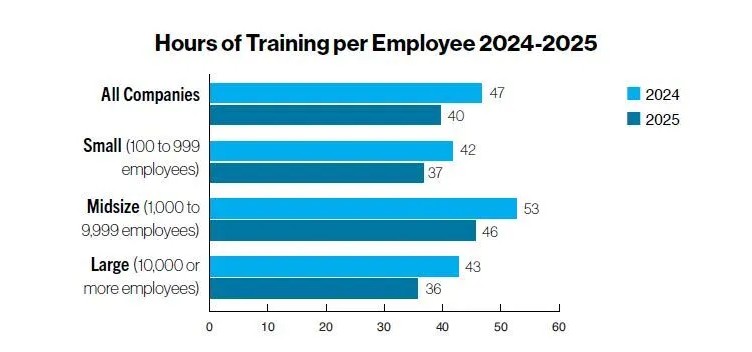
While total spending increased, training time per employee decreased once again. On average, employees received 40 hours of training in 2025, down from 47 hours last year.
By company size, large organizations averaged 62 hours, midsize companies 43 hours, and small firms 42 hours. The service sector provided the most training overall (51 hours on average).
The trend suggests that organizations are focusing on efficiency and precision—delivering shorter, more targeted programs supported by technology, simulations, and on-demand learning.
Learning and development budgets by industry
The percentage of organizations reporting budget increases dropped slightly to 41 percent in 2025, compared to 46 percent in 2024. At the same time, 16 percent reported decreases (up from 14 percent last year), while 43 percent said budgets remained the same.
Most increases were modest: 27 percent of organizations reported gains of 1-5 percent, and 40 percent reported gains of 6-15 percent. The top reasons for budget growth were:
- Increased scope of training programs (65% vs. 57% last year)
- Added training staff (50% vs. 52% in 2024)
- Increased number of learners served (45% vs. 44% last year)
- Purchased new technologies or equipment (43% vs. 38% last year)
Among those with decreases, over half cited a drop of 16 percent or more. Economic uncertainty was the leading reason (58%, down from 74% in 2024), followed by budget adjustments due to efficiencies (36% vs. 26%), reduced training staff (30% vs. 29%), and lower outside trainer investment (21% vs. 10%).
Organizations continued to allocate the largest portions of their training budgets to mandatory compliance training and management/supervisory programs (both at 13 percent), followed by IT/systems and onboarding (each at 11 percent).
For the second consecutive year, management and supervisory training led in planned funding increases (30 percent), followed by AI training (25 percent), interpersonal skills (22 percent), and onboarding (21 percent). Funding for diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) dropped sharply from 24 percent to just 3 percent.
Training delivery in the U.S.
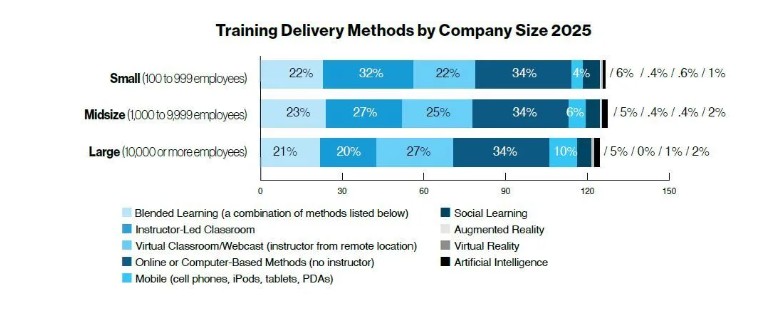
Training delivery methods continued to evolve, with 34 percent of training hours delivered via online or computer-based technologies, consistent with 2024.
Instructor-led classroom training rose slightly to 28 percent (from 27 percent), while virtual classroom/webcasting declined to 24 percent (from 27 percent). Blended learning fell to 22 percent (from 24 percent).
Mobile delivery doubled to 6 percent, and social learning rose to 6 percent. AI-based learning increased to 2 percent, while augmented and virtual reality dipped below 1 percent.
Most organizations (71%) plan to maintain their current balance between in-person and remote learning, with 15 percent expecting to expand in-person formats. The biggest increases are projected in management/supervisory training (24%), interpersonal skills (21%), and executive development (20%).
In terms of technology, the most used platforms were:
- Learning Management Systems (LMSs): 89% (90% last year)
- Virtual classroom/webcasting/video broadcasting: 77% (down from 79%)
- Rapid eLearning tools: 42% (up from 33%)
- Mobile applications: 41% (up from 33%)
- Artificial intelligence: 37% (up from 25%)
- Learning content management systems (LCMSs): 26% (up from 25%)
Mandatory and compliance training remained primarily online, with 92 percent of organizations offering at least some portion online and 45 percent delivering it entirely online.
Types of training for online learning
Across U.S. organizations, online or computer-based delivery accounted for 34 percent of all training hours in 2025, unchanged from 2024. The overall mix of delivery methods continued to strike a balance between efficiency, flexibility, and in-person engagement, with notable shifts toward technology-based learning.
Delivery method split
- Online/computer-based: 34 percent of training hours
- Instructor-led classroom: 28 percent (up from 27 percent in 2024)
- Virtual classroom/webcasting: 24 percent (down from 27 percent)
- Blended learning: 22 percent (down from 24 percent)
- Mobile delivery: 6 percent (up from 3 percent)
- Social learning: 6 percent (up from 5 percent)
- Augmented/virtual reality: less than 1 percent (down from about 3 percent)
- Artificial intelligence-based delivery: 2 percent (up from 0.8 percent)
Use of online training by topic area
Organizations continue to deliver a large portion of training online across multiple skill areas. In 2025, the highest online delivery rates were seen in IT and systems, desktop applications, and diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training.
- IT/systems training: 76 percent
- Desktop application training: 75 percent
- DEI training: 72 percent
- Interpersonal skills training: 70 percent
- Management/supervisory training: 67 percent
- Customer service training: 66 percent
- Professional/industry-specific training: 64 percent
- AI training: 63 percent
- Sales training: 61 percent
- Onboarding: 56 percent
- Executive development: 48 percent (lowest among all categories)
Planned in-person vs. remote balance
Most companies plan to maintain their current mix of in-person and remote training.
- 71 percent of organizations intend to keep the same balance of delivery methods.
- 15 percent plan to increase in-person training; 13 percent plan to increase remote training.
- The largest anticipated increases in in-person sessions are in management and supervisory training (24 percent), interpersonal skills (21 percent), and executive development (20 percent).
Training outsourcing
Average spending on outsourcing declined slightly to $217,178 in 2025, down from $241,311 in 2024. Large companies spent an average of $409,778, midsize companies $309,431, and small companies $112,412. Outsourcing accounted for 7 percent of total training budgets, up from 6 percent last year.
More instruction and facilitation were outsourced than managed internally (62% vs. 38%), with midsize companies outsourcing about 10 percent more than small or large organizations.
Levels of outsourcing are expected to remain steady in 2026, with 85 percent of respondents anticipating no change. Roughly equal numbers of companies plan to increase or reduce outsourcing (7% vs. 8%).
New this year, Training magazine gathered input from 164 training solution providers. The majority focused on professional/industry-specific training (27%), leadership development (26%), and interpersonal skills (13%). Most providers reported increased revenue (42%) and cited growth in AI solutions (29%), eLearning tools/systems (28%), and business skills training (26%).
How much does it cost to train an employee in the UK
Recent data show that UK employers’ investment in training has been under pressure. According to the 2024 Employer Skills Survey, UK organisations spent approximately £1,700 per employee in the previous 12 months, down from about £1,960 in 2022.
For those employees who received training, expenditure was higher — approximately £2,710 per person trained in 2024, compared to roughly £3,250 in 2022.
While job‐specific training remains the predominant form of staff development, tracking of the most common modalities suggests health & safety and onboarding remain widespread.
On e-learning uptake, there remains variation by sector — for example, sectors such as education, public administration and health/social-work continue to show higher use of online training relative to primary sector and utilities, although the latest survey did not publish exact updated percentages by region.
Taken together, the data suggest that while UK employers are still investing in learning and development, per-employee spend has fallen in real terms and budgets remain constrained.
UK L&D budgets and programs
UK’s Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) also conducts an annual survey that examines current practices and trends within learning and development (L&D).
The latest survey which was released in June 2023 found that 45 percent indicated that how much companies spend training employees stayed the same, while 24 percent said that their L&D budgets increased in the last 12 months. Approximately 20 percent reported a net decrease in L&D budgets.
Regarding headcount, 57 percent reported that their L&D headcount stayed the same; 10 percent reported a decline (compared to 32 percent in 2021), and 23 percent reported an increase in number of L&D staff (compared to 18 percent in 2021).
The top 5 most cited L&D priorities in 2023 were:
- Addressing skills gaps (29 percent)
- Linking L&D with organizational development (17 percent)
- Linking L&D with performance management (17 percent)
- Improving the induction/onboarding process (16 percent)
- Identifying changing skills requirements (15 percent)
Learning delivery in UK
According to CIPD’s Good Work Index 2024, perceptions of training and development opportunities are more positive, with over half of respondents feeling they receive the training and information needed to perform their job effectively and have opportunities to develop their skills. Similarly, a comparable proportion of managers agree they have the training and information to manage staff effectively.
The most common types included online learning (42 percent) and informal training, such as on-the-job learning (46 percent) and learning from peers (23 percent). Additionally, 10 percent said they attended external conferences, events, or workshops (see Figure 19).
More formal types of training were mentioned less frequently, such as blended learning, off-the-job training, in-house development, coaching, formal qualifications, and opportunities for secondment, job shadowing, or job rotation. Training specifically focused on emerging technologies, like AI or VR, was rarely mentioned, with only 2 percent referencing it, although it may occur within other forms of learning.
Other employee learning statistics
According to a 2023-2024 report by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), training and development for people managers remain essential.
Enhancing people managers’ understanding of their roles and building their soft skills, such as empathy, are key initiatives for 2024, with 76 percent of HR professionals prioritizing these areas.
Upskilling or reskilling the existing workforce is a primary focus for 53 percent of organizations. This emphasis is critical for two main reasons:
- Employee upskilling and reskilling are among the least successful areas for many organizations. In 2023, only 21 percent of HR professionals reported their organizations were effective in this domain.
- The dual forces of Baby Boomer retirements and the rapid expansion of artificial intelligence capabilities are expected to heighten the need for workforce reskilling.
Tackling L&D challenges
In its 2024 L&D Impact Survey, Hemsley Fraser asked 766 L&D, HR, and talent professionals across the UK and North America from a wide range of sectors and organization sizes about the latest changes in the learning and development landscape.
Top cited key challenges for 2024 included
- Accessibility/technology
- Hybrid/remote working/learning
- Budgets/costs
- Workload
- Buy-in/resistance
- Capacity
- Time/resources
- Strategic alignment
- Engagement/attendance
- AI adoption
- Recruitment/onboarding/retention
- Content fatigue
- Conflicting business priorities
Cognota’s 2024 LearnOps Industry Report also found some similar trends including:
- Only 20 percent of L&D teams report being “strongly aligned” with business strategy.
- 69 percent of respondents prioritize improving productivity and performance as a key goal.
- 65 percent identify limited budgets as a primary challenge.
- 45 percent struggle with stakeholder engagement in the planning and executing L&D initiatives.
Most organizations aim to achieve greater alignment between L&D efforts and corporate objectives by 2025. The Hemsley Fraser report cited that in the United Kingdom:
- Capability development is the leading driver, with 66 percent of organizations identifying it as a key focus area. This reflects the growing need to equip employees with advanced skills and competencies to meet evolving business challenges.
- Talent retention, acquisition, and onboarding rank closely behind at 65 percent, emphasizing the importance of attracting and retaining skilled employees while ensuring a smooth integration into the workplace.
- Employee self-fulfillment and engagement are prioritized by 58 percent of organizations. This highlights the focus on creating a positive work culture that fosters personal growth and job satisfaction.
- Business goals also significantly guide 57 percent of organizations in aligning learning initiatives with overall strategic objectives.
In comparison, in North America:
- Talent retention, acquisition, and onboarding, employee self-fulfillment and engagement, and business goals are equally important, with 54 percent of organizations prioritizing each. This reflects a balanced approach to addressing workforce needs while ensuring alignment with corporate strategy.
At 52 percent, operational success emerges as a distinct driver, underscoring the importance of learning initiatives that directly improve efficiency and performance.
Tackling training course creation challenges with AI
Our experience at LearnExperts has been that slow course creation can be attributed to many reasons, but the number one reason is that the process today is still linear and traditional.
People primarily interview subject matter experts (SMEs) and then translate their knowledge into course content using word processing tools (like Word or PowerPoint). This is a long and manual process that requires expertise.
Other reasons why course creation is slow include company and team size, the complexity of the course content, length of the course, schedules of SMEs, availability of reference materials and the adoption of technology for course creation.
Since the process of creating course content is still very traditional and manual, and we encounter it all the time in our client engagements, we decided to create LEAi, our digital course developer. This AI-enabled tool allows companies to use the material they already have to create well-structured knowledge-sharing and training programs.
With LEAi, you can now create instructor-led training, eLearning, knowledge base articles, virtual class content, presentations, webinars, videos and more in minutes rather than days, weeks or months.
If you are in the market for a course creation tool that will help to grow the number of hours of training per employee you provide while reducing training costs per employee or would like some advice on how to accelerate your L&D program, give us a call!




